42、SpringBoot 源码分析 - SpringMVC源码之SimpleUrlHandlerMapping静态资源处理器二
获取资源
@Nullable
protected Resource getResource(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
String path = (String) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE);//获取前面放入的路径属性
...
path = processPath(path);//处理路径,获取资源名字
...
Resource resource = this.resolverChain.resolveResource(request, path, getLocations());//解析资源
if (resource != null) {
//资源转换
resource = this.transformerChain.transform(request, resource);
}
return resource;
}
解析资源
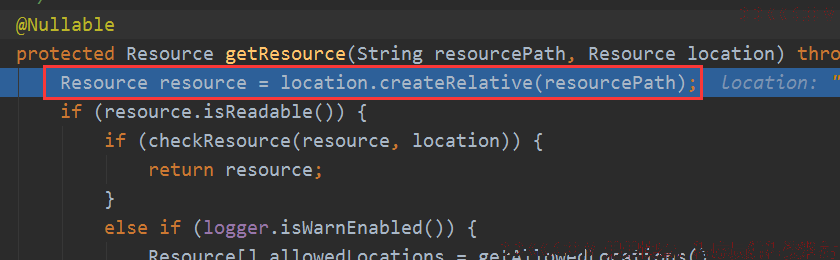
最后到PathResourceResolver的getResource。
@Nullable
private Resource getResource(String resourcePath, @Nullable HttpServletRequest request,
List<? extends Resource> locations) {
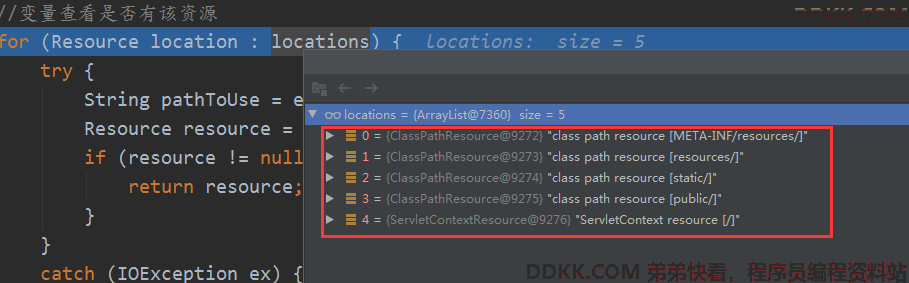
//变量查看是否有该资源
for (Resource location : locations) {
try {
String pathToUse = encodeIfNecessary(resourcePath, request, location);//可能要编码
Resource resource = getResource(pathToUse, location);//获得资源,用URL读取
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String error = "Skip location [" + location + "] due to error";
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(error, ex);
}
else {
logger.debug(error + ": " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
会挨个遍历以下资源路径下是否有该资源。
资源是否可读
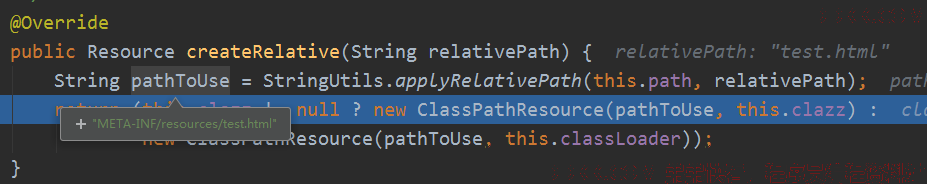
封装路径到该资源路径下,并创建ClassPathResource:
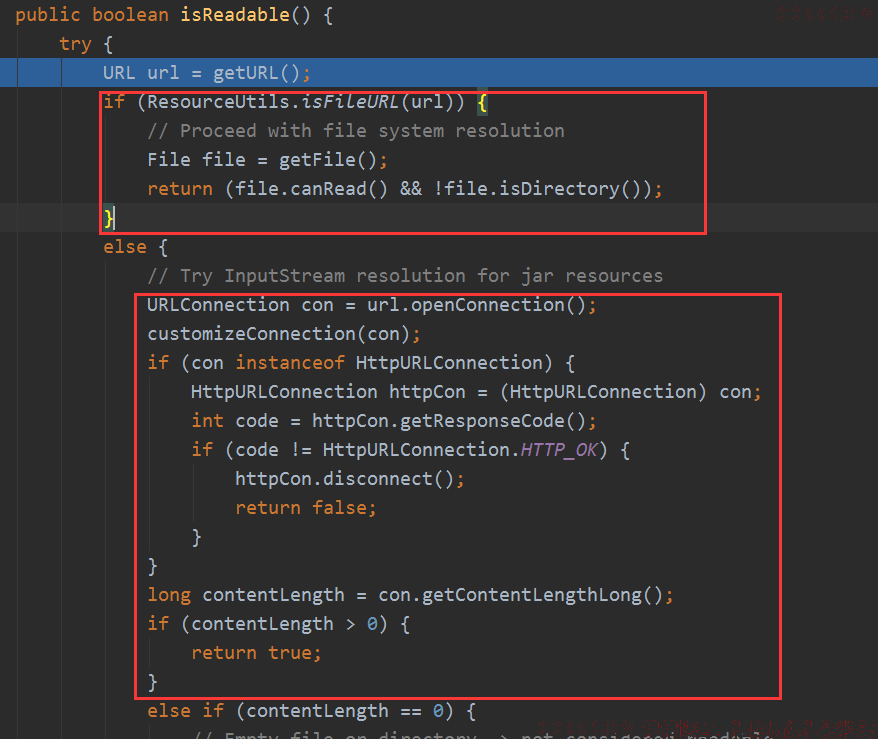
AbstractFileResolvingResource的isReadable
先获取URL判断是文件路径还是网络的,然后分别尝试去查找:
其实就是用类加载器去加载路径,返回URL。
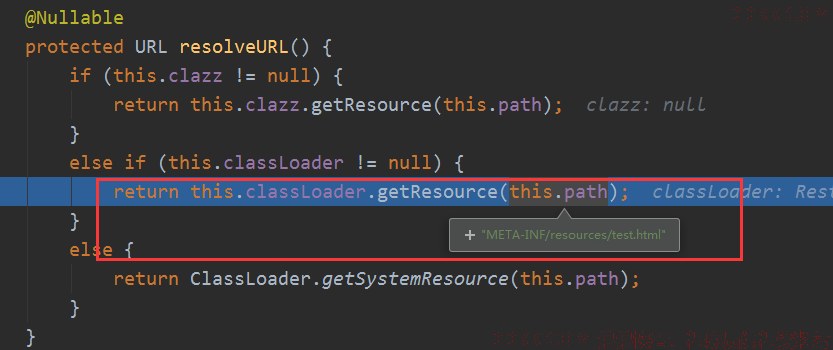
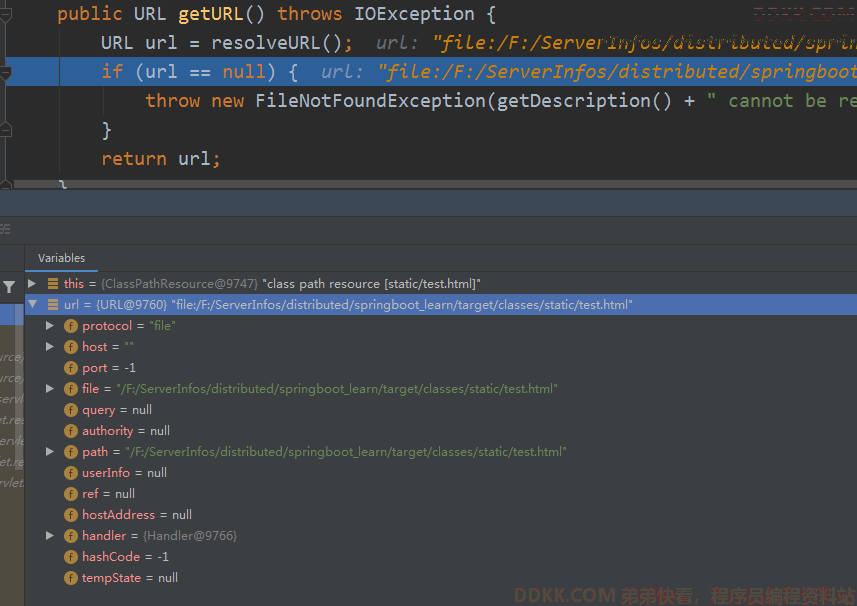
根据协议来判断是不是文件:
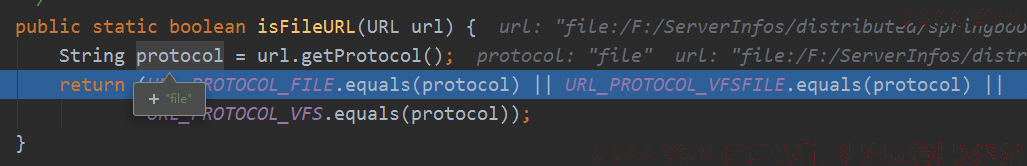
最后创建一个文件对象,看是否可读且不是目录。
如果是网络的话就直接连接,然后获取内容长度来判断存不存在。
写出资源
资源获取到了,要写出去呀,就是调用AbstractHttpMessageConverter的write方法,添加好内容头信息,然后写入输出缓存,并刷出去。
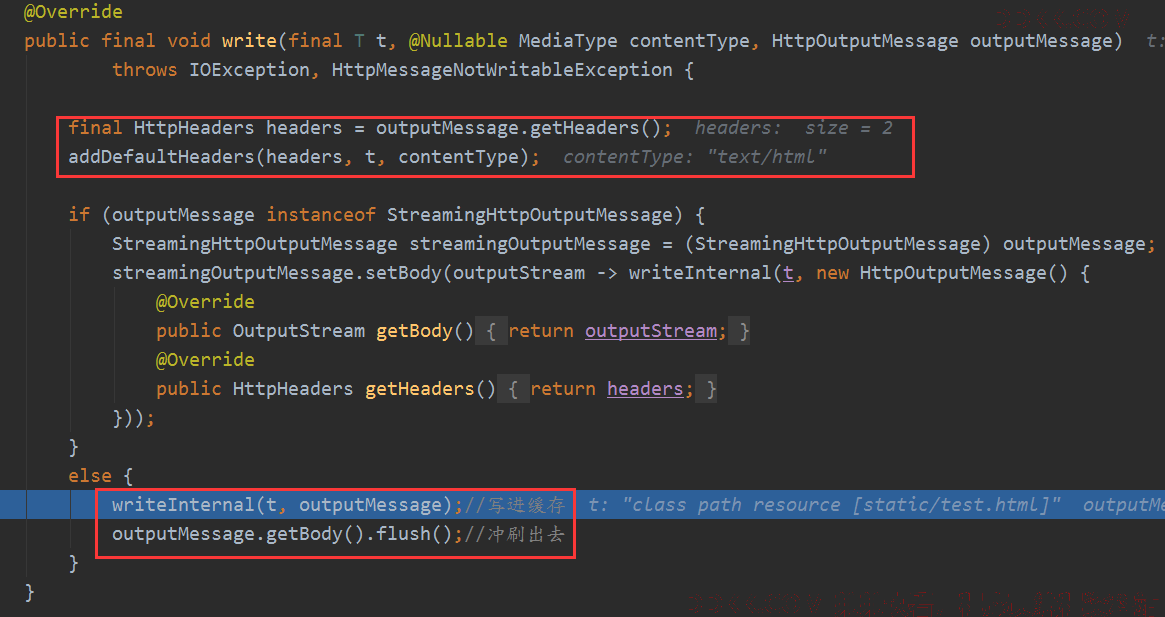
内部就是读资源,然后写入输出流中:
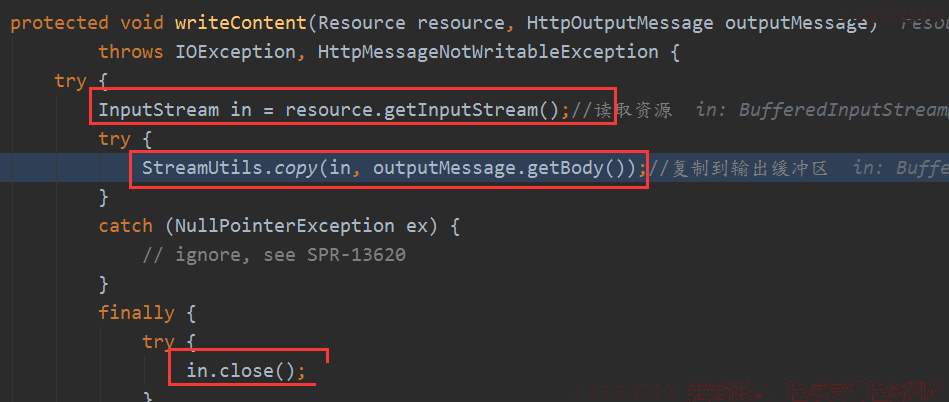
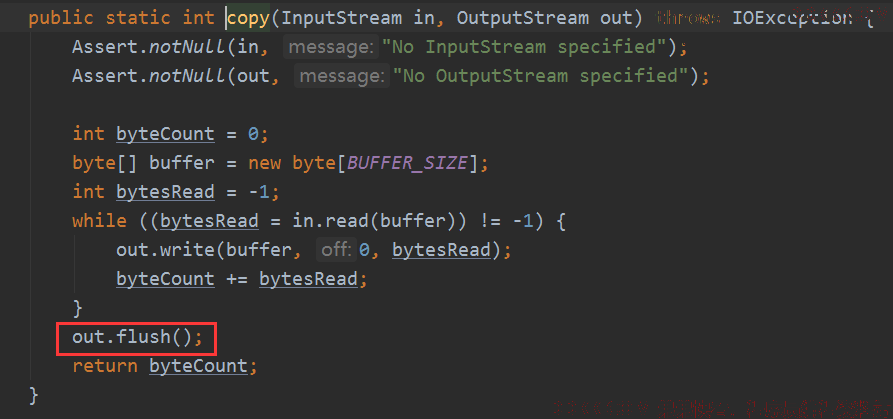
其实他在拷贝数据的时候已经刷出去了:
这样,静态资源的处理流程基本知道了,主要SimpleUrlHandlerMapping是对一些资源路径做了映射处理,有处理器处理,所以可以直接就访问资源:
classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/,/
下次继续讲其他的细节。
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。