16、Python - 迭代器模式
基本介绍
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)是 Java 和 .Net 编程环境中非常常用的设计模式。
这种模式用于顺序访问集合对象的元素,而不需要知道集合对象的底层表示。
特点:提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又无须暴露该对象的内部表示
迭代器模式属于行为型模式。
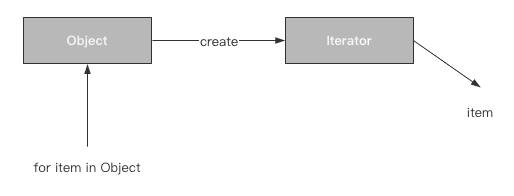
案例图示
一个对象内部的数据存储结构并不能被直接获取到,而是通过迭代器进行获取。
Python本身已经实现了迭代器模式,只需要重写对象中的__iter__()方法和__next__()方法即可。
优缺点
优点:
- 支持以不同的方式遍历一个聚合对象
- 迭代器简化了聚合类
- 在同一个聚合上可以有多个遍历
缺点:
- 由于迭代器模式将存储数据和遍历数据的职责分离,增加新的聚合类需要对应增加新的迭代器类,类的个数成对增加,这在一定程度上增加了系统的复杂性
代码实现
用Python实现迭代器模式,迭代一个二叉树对象:
# 可迭代对象
class BinaryTree:
def __init__(self, root):
self.key = root
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.height = 0
def insertLeft(self, newNode):
tree = BinaryTree(newNode)
if not self.leftChild:
self.leftChild = tree
else:
如果插入位置已有节点,则整体向下挪
新的子节点与旧的子节点链接,旧的父节点与新的子节点链接
tree.leftChild = self.leftChild
self.leftChild = tree
self.height += 1
def insertRight(self, newNode):
tree = BinaryTree(newNode)
if not self.rightChild:
self.rightChild = tree
else:
tree.rightChild = self.rightChild
self.rightChild = tree
self.height += 1
def getRightChild(self):
return self.rightChild
def getLeftChild(self):
return self.leftChild
def setRootVal(self, obj):
self.key = obj
def getRootVal(self):
return self.key
def __iter__(self):
return TreeIterator(tree=self)
def __str__(self):
return "<class 'BinaryTree' value: %r >"%self.getRootVal()
# 迭代器
class TreeIterator:
def __init__(self, tree) -> None:
self.tree = tree
self.treeLst = [self.tree]
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
采用层级遍历
while len(self.treeLst) > 0:
node = self.treeLst.pop(0)
if node.leftChild:
self.treeLst.append(node.getLeftChild())
if node.rightChild:
self.treeLst.append(node.getRightChild())
return node
raise StopIteration("Tree iter end")
if __name__ == '__main__':
binaryTree = BinaryTree("a")
binaryTree.insertLeft("b")
binaryTree.insertRight("c")
binaryTree.leftChild.insertLeft("d")
binaryTree.leftChild.insertRight("e")
binaryTree.rightChild.insertLeft("f")
for node in binaryTree:
print(node)
# <class 'BinaryTree' value: 'a' >
# <class 'BinaryTree' value: 'b' >
# <class 'BinaryTree' value: 'c' >
# <class 'BinaryTree' value: 'd' >
# <class 'BinaryTree' value: 'e' >
# <class 'BinaryTree' value: 'f' >