22、Spring Security 实战 - Spring Security中的密码加密
前言
截止到现在, 已经带各位学习了很多关于Spring Security的知识点,但是Spring Security作为一个安全框架,其中必然就应该带有安全加密方面的内容,所以本篇文章, 就带各位来学习Spring Security中的密码加密机制。
Lets go!
一. 密码加密简介
1. 散列加密概述
我们开发时进行密码加密,可用的加密手段有很多,比如对称加密、非对称加密、信息摘要等。在一般的项目里,常用的就是信息摘要算法,也可以被称为散列加密函数,或者称为散列算法、哈希函数。这是一种可以从任何数据中创建数字“指纹”的方法,常用的散列函数有 MD5 消息摘要算法、安全散列算法(Secure Hash Algorithm)等。
2. 散列加密原理
散列函数通过把消息或数据压缩成摘要信息,使得数据量变小,将数据的格式固定下来,然后将数据打乱混合,再重新创建成一个散列值,从而达到加密的目的。散列值通常用一个短的随机字母和数字组成的字符串来代表,一个好的散列函数在输入域中很少出现散列冲突。在散列表和数据处理时,如果我们不抑制冲突来区别数据,会使得数据库中的记录很难找到。
但是仅仅使用散列函数还不够,如果我们只是单纯的使用散列函数而不做特殊处理,其实是有风险的!比如在两个用户密码明文相同时,生成的密文也会相同,这样就增加了密码泄漏的风险。
所以为了增加密码的安全性,一般在密码加密过程中还需要“加盐”,而所谓的“盐”可以是一个随机数,也可以是用户名。”加盐“之后,即使密码的明文相同,用户生成的密码密文也不相同,这就可以极大的提高密码的安全性。
传统的加盐方式需要在数据库中利用专门的字段来记录盐值 ,这个字段可以是用户名字段(因为用户名唯一),也可以是一个专门记录盐值的字段,但这样的配置比较繁琐。
3. Spring Security中的密码处理方案
那么在Spring Security中,对密码是怎么进行处理的呢?其实Spring Security对密码的处理方案,有如下3种方式:
- 对密码进行明文处理,即不采用任何加密方式;
- 采用MD5加密方式;
- 采用哈希算法加密方式。
3. BCryptPasswordEncoder简介
以上说的是3种密码处理方案,并不代表只有3种加密算法,这个请大家注意哦!
实际上,Spring Security提供了多种密码加密算法,但官方推荐使用的是BCryptPasswordEncoder方案,如下图所示:
我们开发时,用户表中的密码通常是使用MD5等不可逆算法加密后存储,但为了防止彩虹表破解,可以先使用一个特定的字符串(如域名)进行加密,然后再使用一个随机的salt(盐值)加密。其中特定的字符串是程序代码中固定的,salt是每个密码单独随机的,我们一般会给用户表加一个字段单独存储,但这样比较麻烦。
而BCrypt算法却可以随机生成salt并混入最终加密后的密码,验证时也无需单独提供之前的salt,从而无需单独处理salt。不同于 Shiro 中需要自己处理密码加盐,在 Spring Security 中,BCryptPasswordEncoder 本身就自带了盐,所以处理起来非常方便。
另外BCryptPasswordEncoder使用BCrypt强哈希函数,我们在使用时可以选择提供strength和SecureRandom参数 strength值(取值在4~31之间,默认为10)越大,则密钥的迭代次数就越多,密钥迭代次数为2^strength。
二. 利用BCryptPasswordEncoder进行加密
了解了这些基本的理论知识之后,就带各位进行代码实现啦。
我们继续在之前的案例基础之上进行本案例的代码实现,所以项目创建过程略过,请参考之前的章节内容。
1. 编写register接口
为了方便测试,我们首先在UserController中编写一个register接口,用于注册一个新用户,在添加用户时对密码进行加密。
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* 添加用户.这里我们采用表单形式传参,传参形式如下:
* http://localhost:8080/user/register?username=test&password=123
*/
@GetMapping("/register")
public User registerUser(@RequestParam(required = false) User user){
user.setEnable(true);
user.setRoles("ROLE_ADMIN");
//对密码进行加密
user.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(user.getPassword()));
userMapper.addUser(user);
return user;
}
别忘了注入PasswordEncoder对象!
2. 配置密码加密算法
接下来我们在SecurityConfig配置类中,配置到底该采用哪种密码加密算法。我们在SpringBoot环境中是非常容易实现加密算法配置的,只需要创建一个PasswordEncoder对象即可。
@EnableWebSecurity(debug = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
//放行register接口
.antMatchers("/user/register")
.permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/**")
.hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/app/**")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
//对跨域请求伪造进行防护---->csrf:利用用户带有登录状态的cookie进行攻击的手段
.csrf()
.disable();
}
//配置采用哪种密码加密算法
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
//不使用密码加密
//return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
//使用默认的BCryptPasswordEncoder加密方案
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
//strength=10,即密钥的迭代次数(strength取值在4~31之间,默认为10)
//return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(10);
//利用工厂类PasswordEncoderFactories实现,工厂类内部采用的是委派密码编码方案.
//return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
}
注意:
这里我们可以有多种创建PasswordEncoder对象的写法!并且别忘了把“/user/register”注册接口直接放行,注册接口不应该拦截。
3. 测试运行
最后把项目启动起来,测试一下/user/register接口,注册添加一个新的用户,可以看到添加成功后的用户信息返回如下。
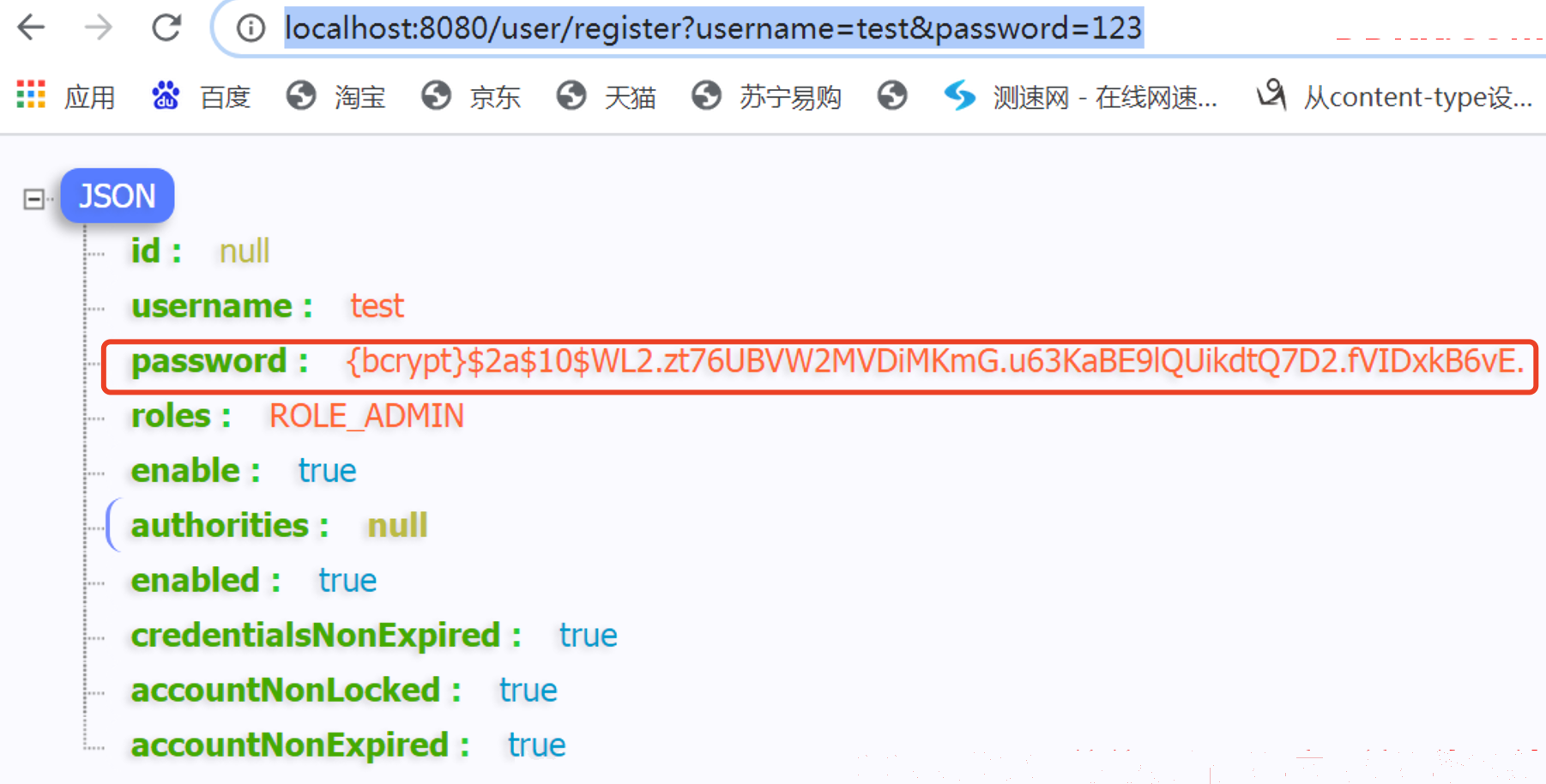
与此同时,我们的数据库中,也有了相关信息:
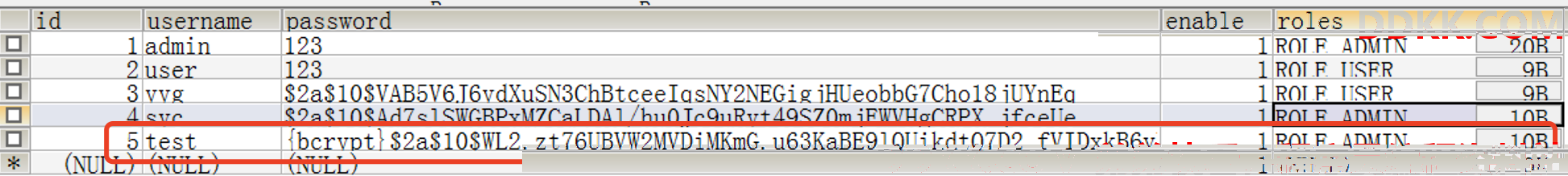
可以看到,我们的密码已经被BCryptPasswordEncoder方案进行了加密,此时我们进行登录时,也需要采用加密的密码才能进行访问了。
4. BCryptPasswordEncoder加解密原理
我前面说过,BCryptPasswordEncoder加密时,每次都会随机生成一个盐值混入到密码中,以此保证即使密码明文一样,最终得到的密文也不一样。但是这时候问题就来了,这个盐值是BCryptPasswordEncoder自动生成的,我们程序员也不知道,那到时候怎么进行密码的比对呢?因为比对密码时,肯定也需要把明文添加盐值后再加密才能比对啊!别急,往下看!
- BCryptPasswordEncoder调用 encode(..) 方法对密码明文加密时,每次都会随机的生成一个盐值,把这个盐值和明文再一起混淆最终得到密码的密文,所以这个最终的密文分为两部分:盐值和最终加密的结果。
- BCryptPasswordEncoder调用matches(..)方法对比的时候,会利用自己特定的方法,先从密文里面拿出盐值,然后利用该盐值对密码的明文进行加密得到一个新的密文,最后利用这个新生成的密文和之前的密文进行对比,这样就能知道传递过来的密码是否和存储的密码是否一样了。
三. 利用其他Encoder进行加密实现
1. MessageDigestPasswordEncoder的用法
除了可以使用上面提到的默认的BCryptPasswordEncoder加密方案之外,我们还可以使用MessageDigestPasswordEncoder方案,该方案内部是采用"MD5"、"SHA-1"、"SHA-256"等信息摘要算法实现的加密,所以我们需要在构造的时候传入MD5等算法名称字符串。这个配置在SecurityConfig类中实现即可!
@Bean
public MessageDigestPasswordEncoder messageDigestPasswordEncoder(){
return new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5");
}
配置好了MessageDigestPasswordEncoder对象,我们就可以利用该encoder对象对密码明文,比如“123”进行加密,就会得到如下密文:
{EUjIxnT/OVlk5J54s3LaJRuQgwTchm1gduFHTqI0qjo=}4b40375c57c285cc56c7048bb114db23
利用MessageDigestPasswordEncoder的encode(..) 加密方法,每次都会随机生成盐值,所以对相同的明文进行多次加密,每次得到的结果是不一样的。
MessageDigestPasswordEncoder这个加密的最终结果也是分为两部分:盐值 + MD5(password+盐值)。那么当我们调用 matches(..) 方法对比密码的时候,也是先从密文中得到盐值,然后利用该盐值再加密明文,最后利用这个新生成的密文和之前的密文进行对比。
2. DelegatingPasswordEncoder的用法
我们还有另一种加密实现写法,就是利用DelegatingPasswordEncoder来进行实现。
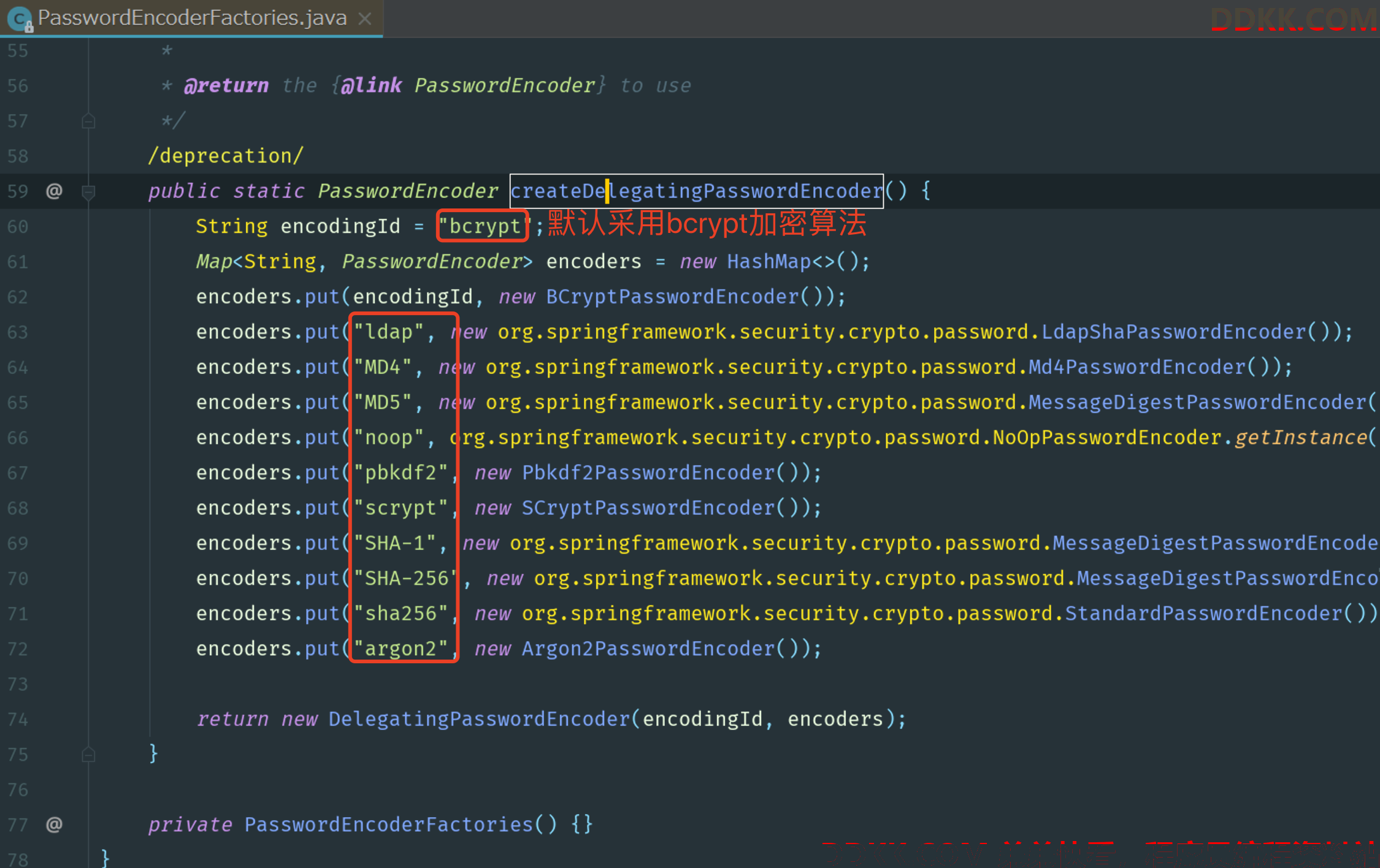
DelegatingPasswordEncoder是Spring Security 推出的一套兼容方案,该方案会根据加密类型的id字符串(idForEncode),去自身缓存的所有加密方式中(idToPasswordEncoder)取出对应的加密方案对象,然后对明文进行加密和密文的对比。DelegatingPasswordEncoder对象的初始化,一般是使用 Spring Security 提供的一个工厂构造方法:
public static PasswordEncoder createDelegatingPasswordEncoder() {
String encodingId = "bcrypt";
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>();
encoders.put(encodingId, new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("ldap", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.LdapShaPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD4", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Md4PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("pbkdf2", new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("scrypt", new SCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("SHA-1", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1"));
encoders.put("SHA-256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256"));
encoders.put("sha256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.StandardPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("argon2", new Argon2PasswordEncoder());
return new DelegatingPasswordEncoder(encodingId, encoders);
}
这个工厂的静态构造方法把常用的几种密码方案都注入到了缓存Map中,默认注入的 encodingId 对应的是 BCryptPasswordEncoder加密方案,这样系统就可以达到在新存储密码可以使用 BCryptPasswordEncoder 加密方案进行加密,但是对于数据库里面以前用其他方式加密的密码也支持比对。我们可以复写该方法,然后修改这个“encodingId”的值,就可以在几种加密算法中进行切换了。
四. 源码解析
利用上面的代码,我们就实现了密码加密,还是很简单的,那么加密的底层原理是怎么样的呢?我们看看源码是怎么定义的吧。
1. PasswordEncoder接口解读
根据上文可知,Spring Security 为我们提供了一套简单易用的密码加密和比对规则,主要是利用org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder 接口来进行实现,在该接口中定义了如下三个方法:
public interface PasswordEncoder {
/**
* Encode the raw password. Generally, a good encoding algorithm applies a SHA-1 or
* greater hash combined with an 8-byte or greater randomly generated salt.
*/
String encode(CharSequence rawPassword);
/**
* Verify the encoded password obtained from storage matches the submitted raw
* password after it too is encoded. Returns true if the passwords match, false if
* they do not. The stored password itself is never decoded.
*
* @param rawPassword the raw password to encode and match
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password from storage to compare with
* @return true if the raw password, after encoding, matches the encoded password from
* storage
*/
boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword);
/**
* Returns true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false. The default implementation always returns false.
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password to check
* @return true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false.
*/
default boolean upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) {
return false;
}
}
在PasswordEncoder接口中,有3个方法如下:
1、**encode()方法,**用于对密码进行加密,参数 rawPassword 表示我们传入的密码明文,返回值是加密之后的密文;
2、**matches()方法,**表示对密码进行比对,参数 rawPassword 代表用户登录时传入的密码,encodedPassword 则代表加密后的密码(一般从数据库中查询而来);
3、upgradeEncoding()方法**,**则用于判断是否需要对密码进行再次加密,以使得密码更加安全, 默认不需要。
2. PasswordEncoder的默认实现子类
该接口有众多的实现子类,而Spring Security默认使用的是BCryptPasswordEncoder这个子类,但注意:默认使用,并不代表就是最优的方案哦!
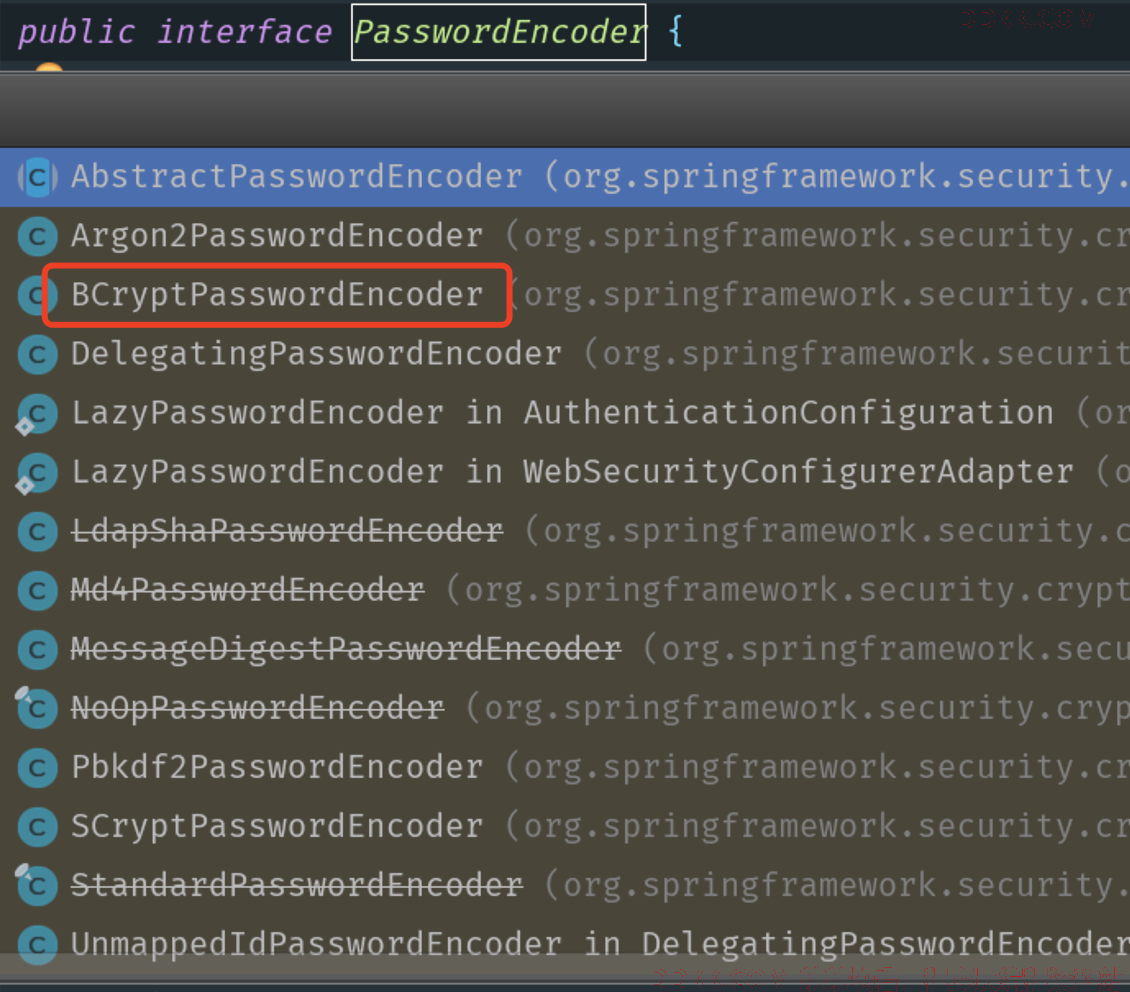
在这些众多实现类中,其中常用的有下面这么几个子类:
- BCryptPasswordEncoder:Spring Security 默认使用的加密方案,使用BCrypt强哈希方法来加密;
- MessageDigestPasswordEncoder:用作传统的加密方式加密(支持 MD5、SHA-1、SHA-256...);
- DelegatingPasswordEncoder:最常用,推荐使用该方案,根据加密类型id进行不同方式的加密,兼容性强;
- NoOpPasswordEncoder:明文,不做加密处理;
- 其他子类。
3. matches()默认的执行时机
密码的加密,肯定需要我们程序员自己选择一个合适的时机进行操作,比如在注册时给用户密码进行加密。这时候你可能会有疑问,我们利用Spring Security默认的登录页面进行登录时,好像咱们自己并没有手动进行密码的对比吧?
对的!Spring Security的登录页面中,密码对比是自动进行的!只要我们配置了BCryptPasswordEncoder或者其他策略,Spring Security都会自动按照我们这个策略进行密码的比对,不需要我们程序员自己编码比对。那么这个自动比对是在哪里实现的呢?我们往下看!
PasswordEncoder接口中有个 matches()方法,默认情况下是由系统自动调用的,当我们基于数据库进行认证授权时,默认是在 DaoAuthenticationProvider#additionalAuthenticationChecks() 方法中调用的。
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
从源码中可以看到,Spring Security的密码比对,首先会从authentication对象中获取密码值,然后通过 passwordEncoder.matches 方法来进行比对,如果比对失败则抛出BadCredentialsException异常,这就是我们登陆时Spring Security的默认密码比对实现。
五. 实现多密码加密方案共存
以上咱们就实现了如何在Spring Security中进行密码加解密了,这就完了吗?还没!Spring Security的密码加解密还有更高级的一个功能!
1. 需求背景
我们进行开发时,经常需要对老旧项目进行改造。这个老旧项目,一开始用的密码加密方案可能是MD5,后来因为种种原因,可能会觉得这个MD5加密不合适,想更新替换一种新的加密方案。但是我们进行项目开发时,密码加密方式一旦确定,基本上没法再改了,毕竟我们不能让用户重新注册再设置一次新密码吧。但是我们此时确实又想使用最新的密码加密方案,那怎么办呢?
这时候,我们就可以考虑使用DelegatingPasswordEncoder来实现多密码加密方案了!
2. 实现过程
2.1 配置DelegatingPasswordEncoder
我们在SecurityConfig配置类中,配置DelegatingPasswordEncoder对象。
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
//利用工厂类PasswordEncoderFactories实现,工厂类内部采用的是委派密码编码方案!
//推荐使用该方案,因为后期可以实现多密码加密方案共存效果!
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
2.2 定义测试接口
为了测试出我们多密码加密共存的效果,我们定义如下3个接口,分别用3种不同的加密方案对密码进行加密。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello, user";
}
/**
* 采用默认的PasswordEncoder,即BCryptPasswordEncoder来加密。
*
* 添加用户.这里我们采用表单形式传参,传参形式如下:
* http://localhost:8080/user/register?username=test&password=123
*/
@GetMapping("/register")
public User registerUser(@RequestParam(required = false) User user) {
user.setEnable(true);
user.setRoles("ROLE_ADMIN");
//对密码进行加密
user.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(user.getPassword()));
userMapper.addUser(user);
return user;
}
/**
* 利用MD5加密密码
*/
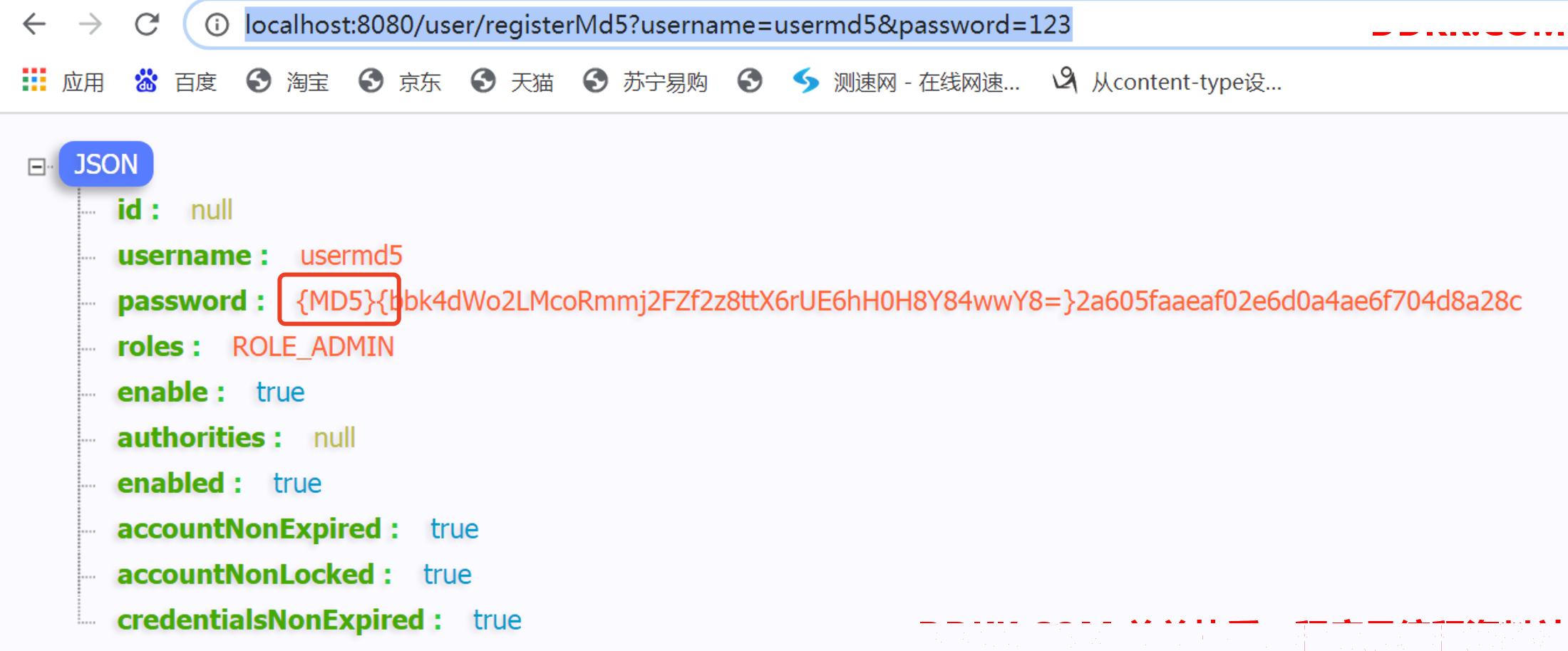
@GetMapping("/registerMd5")
public User registerUserWithMd5(@RequestParam(required = false, name = "username") String username, @RequestParam(required = false, name = "password") String password) {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setEnable(true);
user.setRoles("ROLE_ADMIN");
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>(16);
//encoders.put("bcrypt", new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
//encoders.put("noop", org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
DelegatingPasswordEncoder md5Encoder = new DelegatingPasswordEncoder("MD5", encoders);
//对密码进行加密
user.setPassword(md5Encoder.encode(password));
userMapper.addUser(user);
return user;
}
/**
* 不进行密码加密
*/
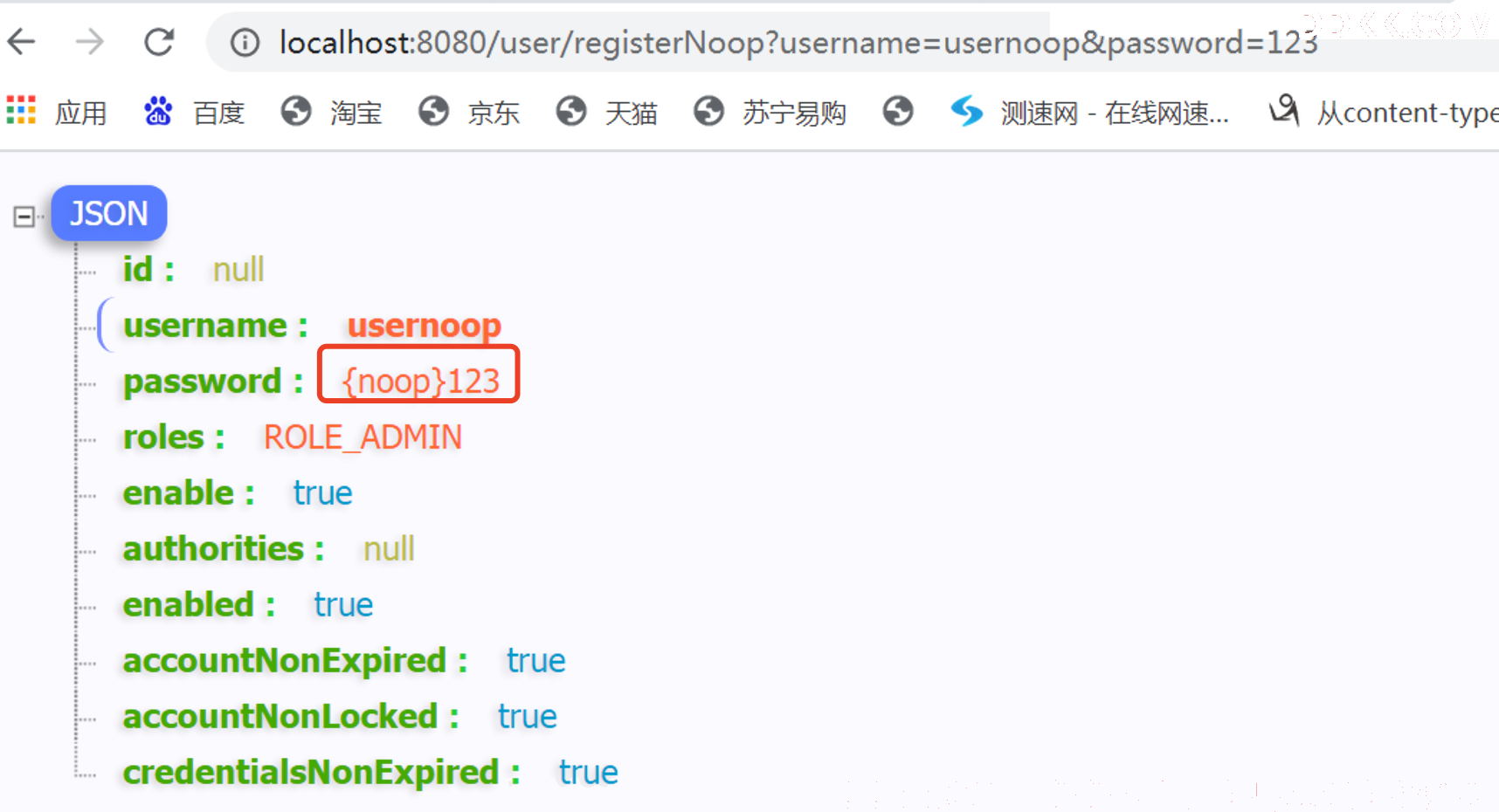
@GetMapping("/registerNoop")
public User registerUserWithNoop(@RequestParam(required = false, name = "username") String username, @RequestParam(required = false, name = "password") String password) {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setEnable(true);
user.setRoles("ROLE_ADMIN");
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>(16);
//encoders.put("bcrypt", new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
//encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
DelegatingPasswordEncoder noopEncoder = new DelegatingPasswordEncoder("noop", encoders);
//对密码进行加密
user.setPassword(noopEncoder.encode(password));
userMapper.addUser(user);
return user;
}
}
2.3 对以上3个接口放行
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
//放行register接口
.antMatchers("/user/register")
.permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/registerMd5")
.permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/registerNoop")
.permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/**")
.hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/app/**")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
//对跨域请求伪造进行防护---->csrf:利用用户带有登录状态的cookie进行攻击的手段
.csrf()
.disable();
}
2.4 测试接口
我们在浏览器中分别请求以上的3个接口,添加3个用户。
添加一个利用MD5加密的密码用户:
添加一个不加密的密码用户:
我的数据库中,此时就会有3个采用不同加密方案的用户了。

然后我们可以分别利用这三个用户进行登录,可以发现在同一个项目中,实现了支持3种不同的密码加密方案的效果。
3. 多密码方案并存的实现原理
Spring Security中为什么可以实现多密码加密方案共存的效果呢?我们来看看源码,探究一下其实现原理。
对于开发者而言,我们通常都是在 SecurityConfig 中配置一个 PasswordEncoder 的实例,类似下面这样:
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
一旦配置好这个PasswordEncoder,剩下的事情,都是由系统调用的,那么系统到底是怎么调用的呢?我们一点点进行剖析。
Spring Security 中,如果我们使用 用户名+密码 的登录方式,密码是在 DaoAuthenticationProvider 中进行校验的,这个我们前面讲过。我们来看下 DaoAuthenticationProvider 中密码是如何校验的:
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
}
可以看到,密码校验就是通过 passwordEncoder.matches 方法来完成的。
那么 DaoAuthenticationProvider 中的 passwordEncoder 对象是从哪里传过来的呢**?**这个对象是不是就是我们一开始在 SecurityConfig 中配置的那个 Bean 呢?接着我们来看下 DaoAuthenticationProvider 中关于 passwordEncoder 的定义,如下:
public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
// =====================================================================================
/**
* The plaintext password used to perform
* PasswordEncoder#matches(CharSequence, String)} on when the user is
* not found to avoid SEC-2056.
*/
private static final String USER_NOT_FOUND_PASSWORD = "userNotFoundPassword";
// ~ Instance fields
// ================================================================================================
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* The password used to perform
* {@link PasswordEncoder#matches(CharSequence, String)} on when the user is
* not found to avoid SEC-2056. This is necessary, because some
* {@link PasswordEncoder} implementations will short circuit if the password is not
* in a valid format.
*/
private volatile String userNotFoundEncodedPassword;
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private UserDetailsPasswordService userDetailsPasswordService;
public DaoAuthenticationProvider() {
setPasswordEncoder(PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder());
}
......
}
从这段代码中可以看到,在 DaoAuthenticationProvider 创建之时,就定义了 PasswordEncoder属性**。在 DaoAuthenticationProvider 创建之时,会设置一个默认的 PasswordEncoder,如果我们没有配置任何 PasswordEncoder,将使用这个默认的 PasswordEncoder;如果我们自定义了 PasswordEncoder 实例,那么会使用我们自定义的 PasswordEncoder 实例!**
那么配置PasswordEncoder的代码是在哪里实现的呢?我们再来看看 DaoAuthenticationProvider 是怎么进行初始化的就知道了**。DaoAuthenticationProvider 的初始化是在 InitializeUserDetailsManagerConfigurer#configure()方法中完成的**,我们一起来看下该方法的源码定义:
class InitializeUserDetailsManagerConfigurer
extends GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
if (auth.isConfigured()) {
return;
}
UserDetailsService userDetailsService = getBeanOrNull(
UserDetailsService.class);
if (userDetailsService == null) {
return;
}
//获取默认的PasswordEncoder对象
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = getBeanOrNull(PasswordEncoder.class);
UserDetailsPasswordService passwordManager = getBeanOrNull(UserDetailsPasswordService.class);
DaoAuthenticationProvider provider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
//设置PasswordEncoder
if (passwordEncoder != null) {
provider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
if (passwordManager != null) {
provider.setUserDetailsPasswordService(passwordManager);
}
provider.afterPropertiesSet();
auth.authenticationProvider(provider);
}
/**
* @return a bean of the requested class if there's just a single registered component, null otherwise.
*/
private <T> T getBeanOrNull(Class<T> type) {
String[] userDetailsBeanNames = InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer.this.context
.getBeanNamesForType(type);
if (userDetailsBeanNames.length != 1) {
return null;
}
return InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer.this.context
.getBean(userDetailsBeanNames[0], type);
}
}
从上面这段代码中我们可以看到:
- SpringSecurity会首先去调用 getBeanOrNull 方法,获取一个 PasswordEncoder 实例,getBeanOrNull 方法实际上就是去 Spring 容器中根据类型来查找对象。
- 接下来直接 new 一个 DaoAuthenticationProvider 对象,大家知道,在 new 的过程中,DaoAuthenticationProvider 中默认的 PasswordEncoder 已经被创建出来了。
- 如果一开始就从 Spring 容器中获取到了 PasswordEncoder 实例,则将之赋值给 DaoAuthenticationProvider 实例,否则就是用 DaoAuthenticationProvider 自己默认创建的 PasswordEncoder。
至此我们就搞明白了Spring Security内部密码方案的处理逻辑了。你学会了吗?评论区留言告诉我吧!