23、MyBatis 源码分析 - session 包
session 包是整个 MyBatis 对外的接口包,也是离用户最近的包。
因为要使用 MyBatis 或者说得到代理对象我们都是在和 session 包中的类进行交互。
// 通过 mybatis 的工具类 Resources 获取配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 将配置文件交给 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 以构建 SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 得到 SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 获取代理后的 UserMapper
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
可以发现其中比较关键的几个类 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、SqlSessionFactory、SqlSession 都是在 session 包中所定义的。
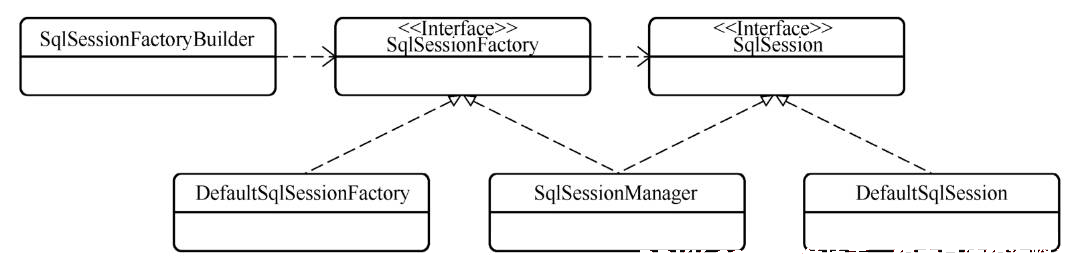
SqlSession 相关类
SqlSession 相关类图
生成 SqlSession
从最开始的示例代码中我们可以发现,要生成一个 SqlSession 需要经过多个步骤,我们只关注和 session 包中进行交互的步骤。
1、 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder传入配置信息;
2、 利用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构建出SqlSessionFactory;
3、 通过SqlSessionFactory开启一个SqlSession;
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// 传入配置文件,创建一个 XMLConfigBuilder 类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
// 解析配置文件,得到配置文件对应的 Configuration 对象
// 根据 Configuration 对象,获得一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("");
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException ignore) {
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
// MyBatis 全局配置信息
private final Configuration configuration;
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
// 从 DataSource 中开启一个会话
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 得到当前 Configuration 的运行环境
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 从缓存中得到事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 构建执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 构建 SqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("");
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
DefaultSqlSession
executor 包是最为核心的执行器包。而 session 包的一个重要的作用就是将这个能力暴露给用户,让用户能使用,所以 DefaultSqlSession 的作用就这个。
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
// MyBatis 全局配置信息
private final Configuration configuration;
// 执行器
private final Executor executor;
// 是否自动提交
private final boolean autoCommit;
// 缓存是否已经被污染
private boolean dirty;
// 游标列表
private List<Cursor<?>> cursorList;
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
return selectList(statement, parameter, rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
}
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
// 得到映射语句
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 调用 Executor 的方法
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("“);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
SqlSessionManager
将SqlSessionManger 和 SqlSession 相关类分开讲解是因为它算是一种工具类,就算不用这个工具类,也能使用 MyBatis。但是在某些场景下使用它可能会更加方便。
并且SqlSessionManager 十分的特殊,因为它同时实现了工厂类和其产品类的接口。
它的一个重要功能就是在内部实现了线程之间 SqlSession 的隔离,也就是会为每一个线程创建不同的 SqlSession,而这个功能也是通过动态代理实现的,可以发现动态代理真的特别强大。
public class SqlSessionManager implements SqlSessionFactory, SqlSession {
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
// 利用 ThreadLocal 存放线程独有的 SqlSession
private final ThreadLocal<SqlSession> localSqlSession = new ThreadLocal<>();
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{
SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) {
return sqlSessionProxy.selectList(statement);
}
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
final SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionManager.this.localSqlSession.get();
// 如果当前线程已经开启了一个 SqlSession 则直接使用
if (sqlSession != null) {
try {
return method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} else {
// 如果没有开启 SqlSession,则创建一个临时使用的 SqlSession
try (SqlSession autoSqlSession = openSession()) {
try {
final Object result = method.invoke(autoSqlSession, args);
autoSqlSession.commit();
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
autoSqlSession.rollback();
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
}
}
}
可以发现是通过 ThreadLocal 实现的线程隔离。
Configuration
在之前的文章中 Configuration 出现了很多次,可以说是老熟人了,但是我们一直都没有深入的去解析它。要知道 mybatis-config.xml 是 MyBatis 配置的入口,而配置文件的根结点就是 <configuration> 节点,因此 Configuration 对象内保存了所有的配置信息。
并且Configuration 类对配置信息进行了进一步的加工,为许多配置项设置了默认值。
而这些可能在 MyBatis 每个地方都有使用到,所以如果很早的就去分析它的话,可能小伙伴们看了也特别的迷茫,估计很快就会跳过去,所以在 session 来分析的话,可以说是刚刚好,因为我们已经将核心的内容都讲解的差不多了。
// <environment> 节点信息
protected Environment environment;
// <<<<<<<<<<< <setting> 节点信息开始 >>>>>>>>>>>
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
// 在值为 null 的时候,是否仍然需要调用对应的 set 方法
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
// 当没有一个属性成功映射时返回空实例
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
protected boolean shrinkWhitespacesInSql;
protected String logPrefix;
protected Class<? extends Log> logImpl;
protected Class<? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
protected Class<?> defaultSqlProviderType;
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString"));
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
protected ResultSetType defaultResultSetType;
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
// 启动了自动映射,但是出现数据库字段找不到对应属性的情况下需要采取的措施
// 有三种方法 没有任何操作、打印异常日志、抛出异常,默认是第一种没有任何操作
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
// 是否启用来加载
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
// <<<<<<<<<<< <setting> 节点信息结束 >>>>>>>>>>>
// <properties> 节点信息
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
// 反射工厂
protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
// 对象工厂
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
// 对象包装工厂
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
// 代理工厂
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); //224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL
// 数据库编号
protected String databaseId;
// 配置工厂,用来创建用于加载反序列化的未读属性的配置
protected Class<?> configurationFactory;
// 映射注册表
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
// 拦截器链(用于支持插件的插入)
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
// 类型处理器注册表,内置了许多,也可以通过 <typeHandler> 节点补充
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry(this);
// 类型别名注册表,内置了许多,也可以通过 <typeAlias> 节点补充
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
// 语言驱动注册表
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
// 映射的数据库操作语句
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
// 缓存
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<>("Caches collection");
// 结果映射,即所有 <resultMap> 节点
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<>("Result Maps collection");
// 参数映射,即所以的 <parameterMap> 节点
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<>("Parameter Maps collection");
// 主键生成器映射
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<>("Key Generators collection");
// 载入的资源,如映射文件资源,防止循环加载
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
// SQL 语句片段,即所有的 <sql> 节点
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
// 存储暂时失败的 select、insert、update、delete 节点的解析
protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<>();
// 存储暂时失败的 cache-ref 节点的解析
protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<>();
// 存储暂时失败的 resultMap 节点解析
protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<>();
// 存储暂时失败的 Method 解析
protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<>();
// 用来存储跨 namespace 的缓存共享设置
protected final Map<String, String> cacheRefMap = new HashMap<>();
Configuration 中的重要方法
在Configuration 不止存储那些配置信息,还提供了一些重要的方法。
创建执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
// 根据执行器类型创建对应的执行器,默认为 SIMPLE
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 如果开启了二级缓存,则还需要封装为 CachingExecutor
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 装载插件
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
创建语句执行器
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 创建统一的 RoutingStatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 插件装载
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
Configuration 中的代码虽然多,但是大部分都非常的简单,都是基于了存储的配置信息又提供了一些增删改查方法。所以就不在过多的讲解。
参考文献
1、 《通用源码阅读指导书:Mybatis源码阅读详解》——易哥;